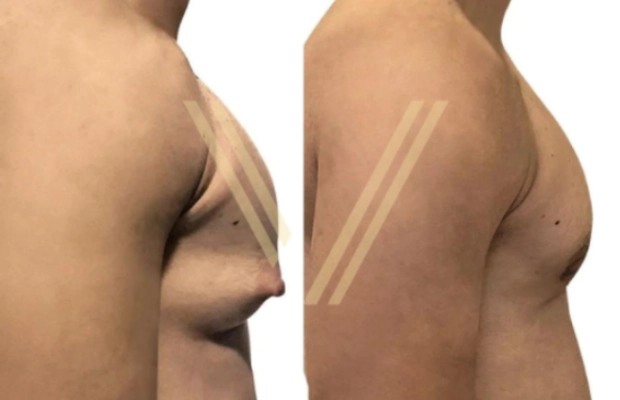
It’s a medical condition characterized by the development of enlarged breast tissue in males as well as fat deposition. It is a common condition that can occur at any age, and its prevalence tends to be higher during adolescence and in older men. Gynecomastia can result from hormonal changes, medical conditions, or the use of certain medications.
Causes of Gynecomastia:
- Hormonal Changes:
- An imbalance in the hormones estrogen and testosterone can lead to the development of gynecomastia. This hormonal imbalance can occur during puberty, aging, or as a result of certain medical conditions.
- Puberty:
- Gynecomastia is relatively common during puberty as hormonal fluctuations can temporarily cause breast tissue enlargement. In many cases, it resolves on its own.
- Aging:
- As men age, there is a natural decline in testosterone levels, and the relative proportion of estrogen may increase, contributing to gynecomastia.
- Medications:
- Certain medications can cause gynecomastia as a side effect. These may include some antipsychotic medications, anti-androgens, certain antibiotics, and medications used in the treatment of prostate cancer.
- Health Conditions:
- Conditions affecting the testes, adrenal glands, or pituitary gland can disrupt hormone balance and contribute to gynecomastia.
- Substance Use:
- The use of substances such as anabolic steroids, marijuana, and certain drugs can increase the risk of gynecomastia.
Treatment Options for Gynecomastia:
- Observation:
- In cases where gynecomastia is related to puberty, it generally resolves on its own. Observation and monitoring may be recommended.
- Medication:
In some cases, medications can be tried .There are 3 classes of medical treatment – androgens (testosterone, dihydrotestosterone, danazol), anti-estrogens (clomiphene citrate, tamoxifen), and aromatase inhibitors such as letrozole and anastrozole. They are prescribed only in specific conditions where cause is identified.
3- The treatment for each Grade differs depending on the amount of skin excess and ptosis.
- Grade I: Small enlargement, no skin excess
- Grade IIa: Moderate enlargement, no skin excess
- Grade IIb: Moderate enlargement with extra skin
- Grade III: Marked enlargement with extra skin
- .Surgery (Gynecomastia Surgery or Reduction Mammoplasty):
- Surgical intervention may be considered for persistent or severe cases of gynecomastia. The surgical procedure involves the removal of excess breast tissue and, if necessary, liposuction to contour the chest as well as excess skin correction in severe grades.
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Addressing underlying factors, such as substance use or the use of medications contributing to gynecomastia, may be part of the treatment plan.
Consultation with a Healthcare Professional:
It’s important for individuals with concerns about gynecomastia to consult with a healthcare professional, typically a primary care physician or a specialist such as an endocrinologist or a plastic surgeon. The healthcare provider can conduct a thorough evaluation, including a medical history, physical examination, and, if necessary, additional tests to determine the underlying cause and recommend an appropriate course of action.